What is Bell’s Palsy?
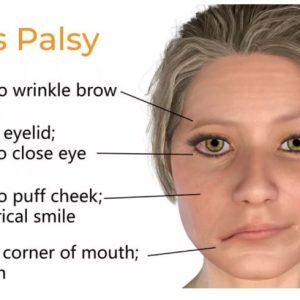
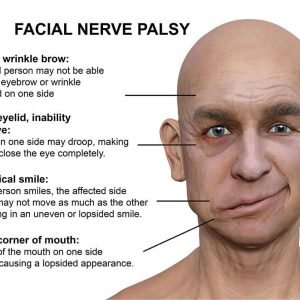
Bell’s Palsy is a condition characterized by temporary weakness or paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face. It occurs when the seventh cranial nerve, known as the facial nerve, becomes inflamed or compressed. The exact cause of Bell’s Palsy is not always clear, but it is thought to be related to viral infections, particularly the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which causes cold sores.
Is Bell’s palsy caused by stress?
People at risk of developing Bell’s palsy are those suffering from stress or who don’t get enough rest, diabetics and people who have experienced respiratory conditions, such as a common cold or the influenza virus.
Can Bell’s palsy go away?
Symptoms usually start to improve within a few weeks, with complete recovery in about six months. A small number of people continue to have some Bell’s palsy symptoms for life. Rarely, Bell’s palsy occurs more than once
You can use artificial tears (eye drops) as often as every hour during the day to keep the eye moist. A moisturizing eye ointment is typically used at night. You can use the ointment during the day, although it will make your vision blurry
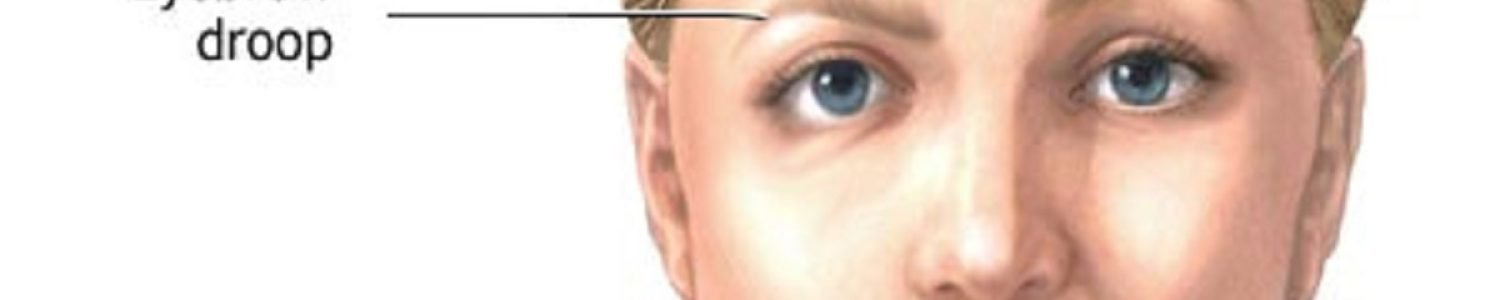
Bell’s palsy usually resolves in time and causes no long-term complications. However, during the illness most people with Bell’s palsy are unable to close their eye on the affected side of their face. It is, therefore, important to protect the eye from drying at night or while working at a computer.
Inflammation and compression of your seventh cranial nerve is the main cause of Bell’s palsy. The seventh cranial nerve carries nerve signals that control your facial movements and expressions. It also carries nerve signals involved in taste and producing tears in your eyes.
In summary, this study provided significant evidence for abnormal brain activity between patients with early left and right Bell’s palsy. In addition, the severities of the disease were closely associated with abnormal fALFF values in certain brain regions.
Bell’s palsy is a paralysis or weakness of the muscles on one side of the face, with young adults of either sex more susceptible for unknown reasons. The facial nerve services the muscles of the face, the ear, salivary and tear glands, and provides some of the sensations of taste on the tongue.
Skip The Waiting Room!
Register Online Before You Arrive.
We have up to date schedules, contact information, & let you book appointments online.